Oats help control blood sugar levels
It is worth emphasising the quality of carbohydrates because it has a great deal of significance in terms of coping. Some carbohydrates raise and lower blood sugar levels sharply and quickly, while some others will help maintain blood sugar levels for a long time.
Stable, permanent blood sugar levels promote general well-being and help to maintain alertness. It is also good for brain functioning. The brain uses glucose from the blood, or blood sugar, up to an amount of about 120-140 grams per day. Large fluctuations in blood sugar levels are tiring. Concentration, attention and observation may also be difficult.
Carbohydrates that raise and lower blood sugar levels quickly are found, for example, in low-fibre bread and in products with a high sugar content. Beta-glucan in oats and other cereal fibers, on the other hand, are slow carbohydrates that help balance out fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
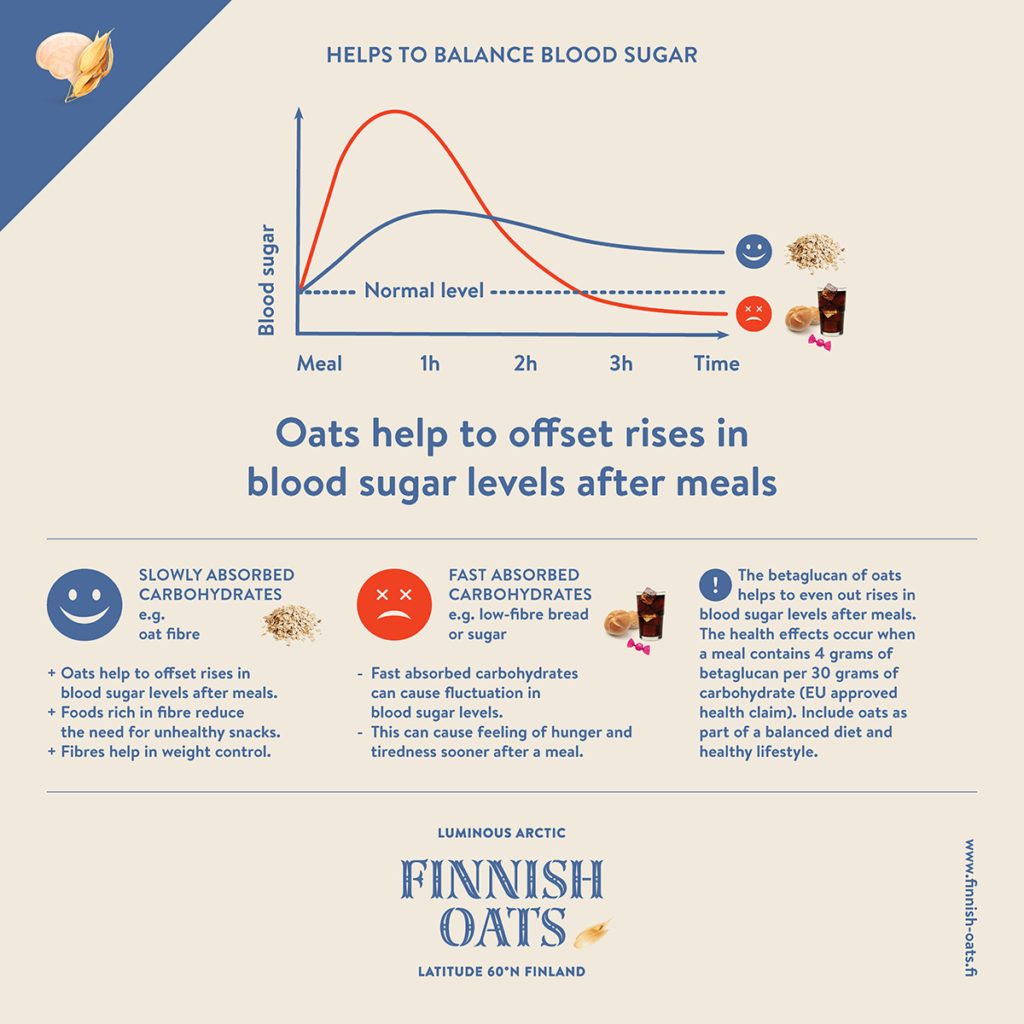
The EU has approved a health claim for oats that state its influence in evening out blood sugar levels:
The Beta-Glucan of oats helps to even out rises in blood sugar levels after meals. The health effects occur when a meal contains 4 grams of Beta-glucan per 30 grams of carbohydrate.

